Experts Warn Advanced Evasion Strategies
[ad_1]
Cyber security researchers have uncovered a previously undocumented type of ransomware called Rorschach it’s sophisticated and fast.
“What makes Rorschach stand out from other types of ransomware is its high level of customization and technically unique features that have never been seen before in a ransomware,” Check Point Research said in a new report. “In fact, Rorschach is one of them fastest ransomware strains ever observed, in terms of encryption speed.”
The cybersecurity firm said it observed the ransomware used against an unnamed US-based company, adding that they found no branding or overlap linking it to any previously known ransomware perpetrators.
However, further analysis of Rorschach’s source code revealed similarities to the Babuk ransomware, which suffered a leak in September 2021, and LockBit 2.0. Additionally, the ransom notes sent to victims appear to be inspired by Yanluowang and DarkSide.
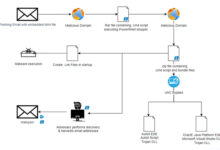
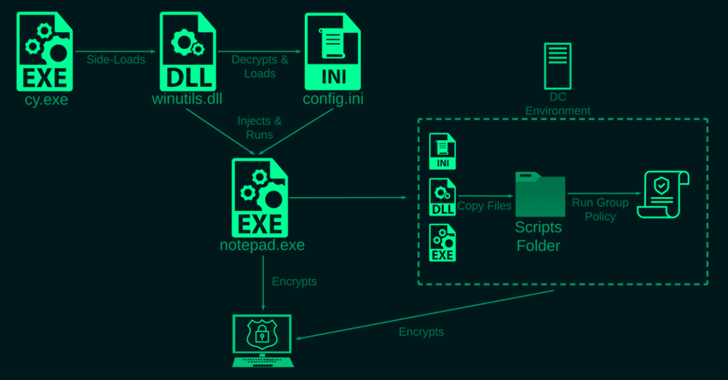
The most significant aspect of intrusion is the use of so-called techniques ETC side loading to load the ransomware payload, a method rarely observed in such an attack. The development marks a new sophistication in the approach adopted by financially motivated groups to avoid detection.
Specifically, the ransomware is said to have been used by abusing Palo Alto Network’s Cortex XDR Dump Service Tool (cy.exe) to sideload a library named “winutils.dll.”
Another unique characteristic is its highly customizable nature and use of direct syscalls to manipulate files and bypass defense mechanisms.
The Rorschach ransomware is also tasked with terminating predefined lists of services, removing shadow and backup volumes, cleaning Windows event logs to remove forensic traces, disabling Windows firewall, and even deleting itself after completing its actions.
Internal propagation is achieved by compromising the domain controller and creating a group policyaccording to Check Point and South Korean cybersecurity company AhnLab, which is wrong associated infection chain to DarkSide earlier this February.
Ransomware, like other types of malware observed in the wild, skip machine located in Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) countries by checking the system language.
“Rorschach ransomware uses a very effective and fast hybrid cryptographic scheme, which combines the curve25519 algorithm and the eSTREAM cipher hc-128 for encryption purposes,” explain researchers Jiri Vinopal, Dennis Yarizadeh, and Gil Gekker.
This process is designed to encrypt only a certain portion of the original file’s contents instead of the entire file, and uses additional compiler optimization methods that make it a “speed demon”.
In five separate tests conducted by Check Point in controlled environments, 220,000 files were encrypted using Rorschach in an average of four minutes and 30 seconds. LockBit 3.0, on the other hand, takes about seven minutes.
“Its developers implemented new anti-analysis and defense evasion techniques to evade detection and make it more difficult for security software and researchers to analyze and mitigate the impact,” the researchers said.
“On top of that, Rorschach appears to have taken some of the ‘best’ features from some of the leading ransomwares leaked online, and integrated them all together. In addition to Rorschach’s self-propagating capabilities, it raises the bar for ransom attacks.”
The findings come as Fortinet FortiGuard Labs detailed two new ransomware families named PayMe100USD, a Python-based file locking malware, and Dark Power, written in the Nim programming language.
Rorschach (aka BabLock) Attacks Seen in Asia, Europe, and the Middle East
Singapore-headquartered Group-IB said it had identified a Rorschach attack targeting small and medium enterprises as well as industrial enterprises in Asia, Europe and the Middle East.
Become an Incident Response Pro!
Unlock the secrets to bulletproof incident response – Master a 6-Phase process with Asaf Perlman, Cynet’s Lead IR!
The cybersecurity firm has named the ransomware strain BabLock, so named because of the similarity of its source code to Babuk and LockBit. It is said to be active since at least June 2022 and has the ability to attack ESXi and Linux systems as well.
“The absence of (data leak sites), together with relatively modest ransom demands ranging from 50,000 to 1,000,000 USD, allows the group to operate quietly and stay under the radar,” Group-IB researchers Andrey Zhdanov and Vladislav Azersky said.
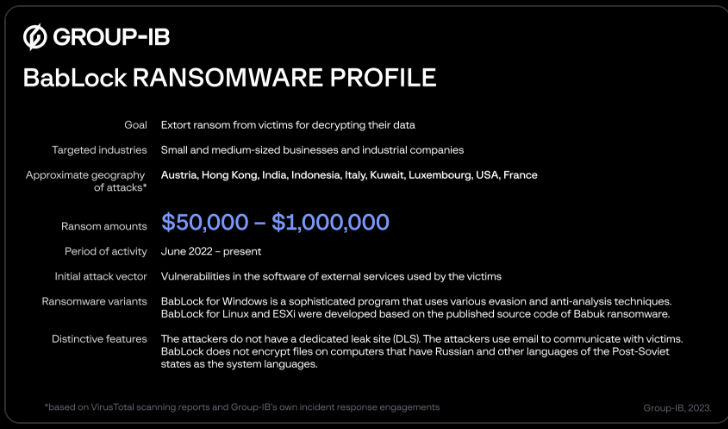
In an incident targeting an unnamed industrial sector company in Europe, the threat actor took advantage of a remote code execution flaw impacting Zimbra Collaboration (CVE-2022-41352, CVSS score: 9.8) to gain early access.
The attack does not require data exfiltration prior to encryption, but instead pressures the victim to pay by threatening to “attack your company again in the future” and “wipe all your data from your network”.
The Linux counterpart, according to Group-IB, is a 32-bit ELF binary written in Go 1.18.3, while the ESXi variant is a 64-bit program for Linux in ELF format compiled using the GNU Compiler (GCC). Both versions are based on the leaked Babuk ransomware source code.
“It would make more sense for threat actors to use simpler programs based on Babuk to encrypt Windows systems, but they would prefer to develop their own, more sophisticated programs, which are overall not similar to other families,” the researchers said.
Palo Alto Networks, in an information bulletin released on April 4, said it was aware of an attack that leveraged the Cortex XDR Dump Service Tool to load Rorschach payloads, adding that the attack did not affect macOS and Linux platforms. It is also expected to release a patch to address this issue next week.
“When removed from its installation directory, the Cortex XDR Dump Service Tool (cydump.exe), which is included with the Cortex XDR agent on Windows, can be used to load untrusted dynamic link libraries (DLLs) by a technique known as DLL side-loading, ” cyber security company said.
“Rorschach ransomware uses a copy of this tool and this technique to avoid detection on systems that do not have sufficient endpoint protection. When the Cortex XDR agent is installed in Windows and the Cortex XDR Dump Service Tool process runs from the installation path, it is not possible to load the DLL with this technique.”
[ad_2]
Source link