Development of capable AI-based mass spectrometry techniques
[ad_1]
1. The National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS) has developed an AI-based mass spectrometry technique capable of determining the monomer sequence of a polymer. This technique may be useful for gaining a deeper understanding of basic polymer structures, facilitating the development of new materials and helping to solve plastic recycling problems.
1. The National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS) has developed an AI-based mass spectrometry technique capable of determining the monomer sequence of a polymer. This technique may be useful for gaining a deeper understanding of basic polymer structures, facilitating the development of new materials and helping to solve plastic recycling problems.
2.Polymers are very large molecules made up of chains of many (ranging from hundreds to hundreds of thousands) of smaller molecules called monomers bonded together. Many common polymers (for example, plastics and resins) are copolymers, consisting of several types of monomers. During the copolymerization process, the monomers are arranged stochastically along the main chain, resulting in a sequence distribution. Since the distribution of these sequences is thought to greatly influence the material performance of copolymer materials, the development of polymer sequencers—an analytical method for quantitatively evaluating distribution—has been awaited as a potentially effective tool for innovative polymeric materials.
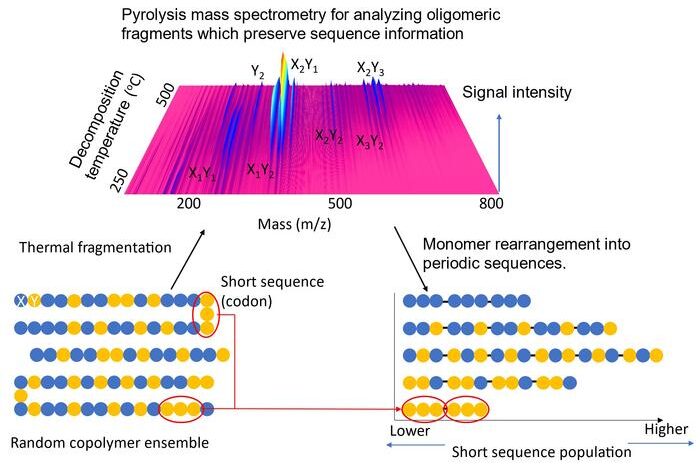
3. This research team recently developed the world’s first practical polymer sequencing that measures short monomer segments in specific sequences, here called “codons” using the analogy of nucleotide triplets, via pyrolysis mass spectra. In this technique, the analyte copolymer is heated gradually from room temperature to 600HiC, successively produced oligomer fragments to be recorded by mass spectrometry according to their heat susceptibility. Based on the fragment pattern, virtual copolymers repeating single codon species were reconstructed via AI analysis, enabling quantification of codon composition in the analytes. This polymer sequencer is applicable to a wide range of versatile monomer combinations. In addition, polymer sequencers can be used to analyze various other materials whose fragments evaporate during heat treatment. This includes insoluble or non-liquidable sample materials and composites with inorganic constituents.
4. The research team plans to investigate the correlation between sequence distribution and copolymer properties and develop a sequence-controlled polymerization technique, using the developed polymer sequencer as the main technology. These efforts can improve the performance of various polymeric materials and solve environmental problems caused by plastics.
***
5. The project was implemented by a research team led by Masanobu Naito (Macromolecule Field Director, Center for Macromolecules and Biomaterials Research (RCMB), NIMS) and Yusuke Hibi (Postdoctoral Researcher, RCMB, NIMS). This work was financially supported by the JST CREST Strategic Basic Research Program as part of the research project “Development of revolutionary materials by combining experimentation with theory/data science”.
6. This research was published in Chemical Science on March 21, 2023, Japan Time.
Research methods
Experimental study
Research Subjects
Not applicable
Article title
Data-driven sequencer that uncovers latent “codons” in synthetic copolymers
Article Publication Date
21-Mar-2023
[ad_2]
Source link